Putin unlikely to be deterred by setbacks, intelligence officials tell House committee
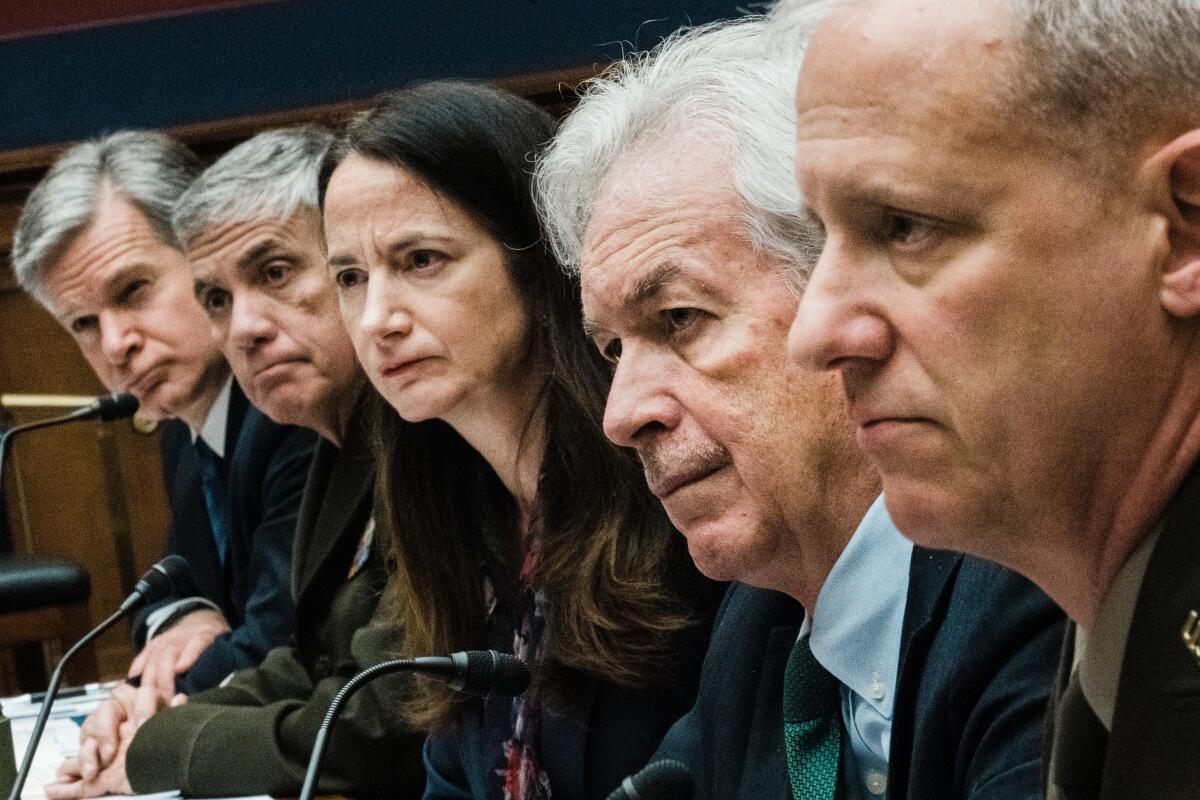

WASHINGTON — Director of National Intelligence Avril Haines told lawmakers Tuesday morning that Russian President Vladimir Putin did not expect the level of Ukrainian resistance to his invasion, nor the level and speed of sanctions imposed by countries around the world.
“Our analysts assess that Putin is unlikely to be deterred by such setbacks and instead may escalate, essentially doubling down,” she said.
The comments from Haines and other intelligence officials came in an unusually candid public hearing with members of the House Intelligence Committee. The hearing was expected to focus on the intelligence community’s annual global threat assessment, but it was instead largely dominated by questions about Russia’s two-week-old invasion of its neighbor Ukraine. The House panel will get a classified assessment in the afternoon.
Haines said Putin likely expected the conflict to last a matter of days at most and predicted Russia will be hard pressed to hold any ground it gains.
“We assess Putin feels aggrieved the West does not give him proper deference and perceives this as a war he cannot afford to lose, but what he might be willing to accept as a victory may change over time given the significant costs he is incurring,” she said.
CIA Director William Burns agreed, saying Putin initially believed Ukraine was weakened and easily intimidated, and that the Russian leader had modernized his military to the point of ensuring a quick victory. Burns added that Putin had been confident early on that he had sanction-proofed his economy, and that the Europeans were too distracted to pay much attention to the invasion.
“He’s been proven wrong on every count,” Burns said.
Still, Burns said the invasion is a “matter of deep personal conviction” for Putin.
“He has been stewing in a combustible combination of grievance and ambition for many years,” Burns said.
Putin’s plan was premised on seizing Kyiv within the first two days of the campaign, Burns said, and he is getting increasingly frustrated at the lack of progress.
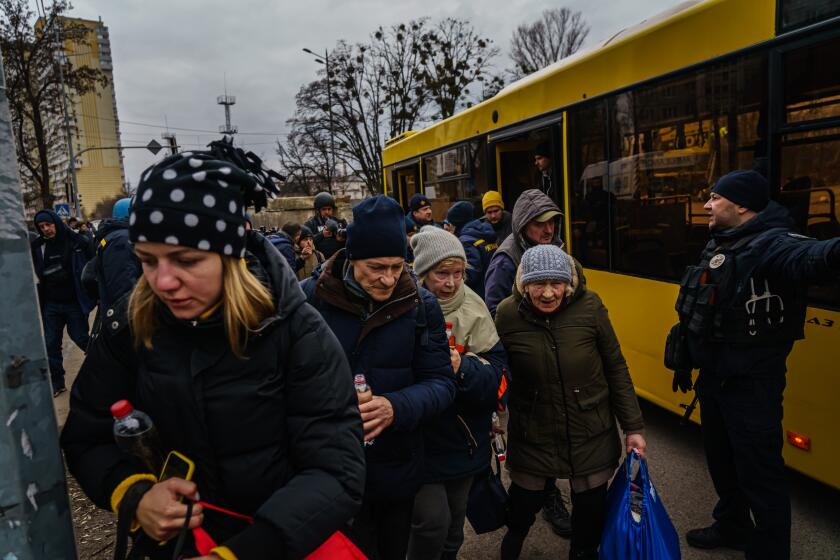
“He’s likely to double down and try to grind down the Ukrainian military with no regard for civilian casualties,” Burns said. “He has no sustainable political endgame in the face of what is going to continue to be fierce resistance from Ukrainians.”
At this point, Burns said he cannot see how Putin can stand up a puppet regime in the face of massive opposition from the Ukrainian people, warning there is an “ugly next few weeks” ahead.
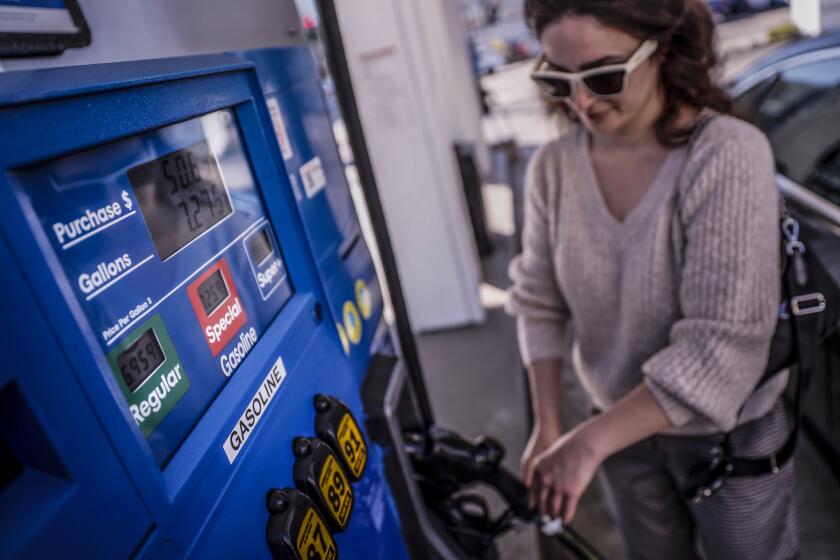
Q&A: How President Biden’s decision to halt U.S. purchases of Russian oil is likely to affect prices at the pump and beyond?
Defense Intelligence Agency Director Lt. Gen. Scott Berrier estimated that 2,000 to 4,000 Russian soldiers have died in the less than two weeks since the invasion began, a number that far exceeds what the Russian government has acknowledged. For context, the United States suffered more than 7,000 military deaths over two decades in Iraq and Afghanistan.
Berrier said Russia appears to be attempting to cut off food and water to Kyiv as a strategy.
“It will become somewhat desperate in I would say 10 days to two weeks,” he said.
Intelligence Committee Chairman Rep. Adam Schiff (D-Burbank) told reporters after the hearing that as Putin doubles down on Ukraine, it remains difficult to see how the conflict ends.
A no-fly zone to protect Ukraine from Putin’s bombs would involve complex ground operations and risk U.S.-Russian conflict and wider war in Europe.
“What’s the offramp? I think what we can do is just to continue to escalate the price that he and Russia have to pay for this,” Schiff said. “I think until he feels that his own regime is at risk, it’s hard to see him looking for an exit ramp.”
Congressional lawmakers are debating how much additional aid to send to Ukraine, and what additional economic measures to take against Russia, which is already seeing unprecedented sanctions on its financial systems, top leaders and businesses. On Tuesday, President Biden announced a ban on the import of Russian oil and energy products into the United States.
Senate Majority Leader Charles E. Schumer (D-N.Y.) has called for some $12 billion in aid, and urged passage this week, saying it “will provide both humanitarian and military assistance for Ukraine: funding for refugees, medical supplies, emergency food supplies, as well as funding to support weapons transfers into Ukraine, and help for our eastern flank NATO allies.”
House Speaker Nancy Pelosi (D-San Francisco) has said Congress is looking to pass $10 billion in emergency aid for Ukraine as part of a larger government funding measure. A vote could occur as soon as today.
More to Read
Get the L.A. Times Politics newsletter
Deeply reported insights into legislation, politics and policy from Sacramento, Washington and beyond. In your inbox three times per week.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.